A new study reveals that the enzyme ADAM19 plays a vital role in controlling inflammatory signals from aging cells in the gut. By inhibiting this enzyme in fruit flies, mice, and human cells, researchers reduced inflammation and signs of cellular aging, offering a potential new treatment pathway for age-related gut disorders that focuses on altering cell behavior rather than destroying the cells themselves.
A Revolutionary Step in Anti-Aging Science
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unveiled a novel treatment that not only repairs the gut but also rejuvenates aging cells. This dual-action therapy targets the root causes of aging, offering promising avenues for combating age-related diseases.
The Science Behind the Breakthrough
Aging is often accompanied by chronic inflammation and cellular senescence—where cells cease to divide and function properly. This new treatment addresses these issues by restoring youthful levels of a key enzyme, telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), which plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular health.
Gut Health: The Foundation of Longevity
The gut is central to overall health, influencing everything from digestion to immunity. As we age, the gut’s integrity can decline, leading to increased inflammation and disease risk. The treatment has been shown to repair gut lining and reduce inflammation, thereby enhancing nutrient absorption and immune function. Dailyscitech
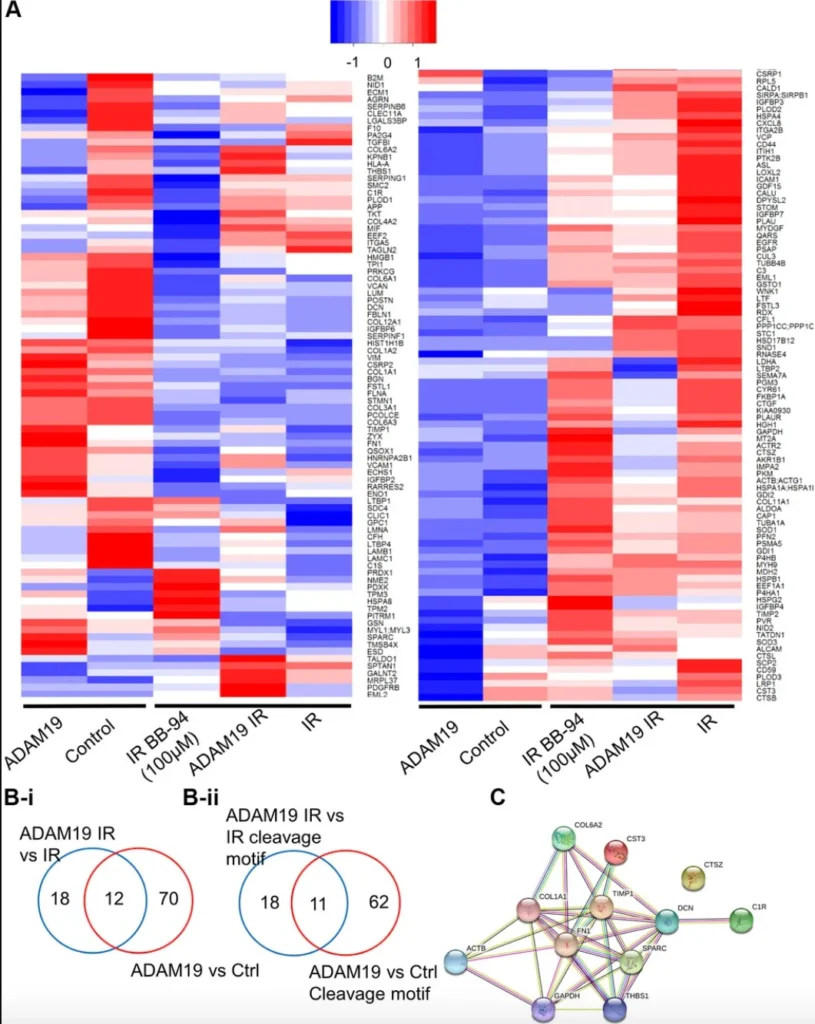
Figure 4. ADAM19 knockdown or inhibition alters secretory factors from senescent cells. (A) Heat map showing changes in the secretome composition from senescent IMR-90 cells with or without ADAM19 shRNA. (B-i) Venn diagram shows altered protein between ADAM 19 vs. IR and IR only groups. (B-ii) Venn diagram shows altered protein with cleavage motif in groups between ADAM 19 vs. IR and ADAM19 vs. control. (C) Protein network 12 commonly altered protein in groups between ADAM 19 vs. IR and IR. Credit: 2025 Bar et al.
Rejuvenating Aging Cells
Beyond gut health, the therapy reactivates TERT, leading to the rejuvenation of aging cells. This reactivation reduces cellular senescence and promotes the formation of new neurons, improving cognitive and muscle functions in preclinical models. Dailyscitech
Implications for Age-Related Diseases
By addressing both gut health and cellular aging, this treatment holds potential for preventing or mitigating age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cardiovascular conditions. The dual-action approach could revolutionize how we approach aging and longevity. Dailyscitech
Reference: “Inhibition of the metalloprotease ADAM19 as a novel senomorphic strategy to ameliorate gut permeability and senescence markers by modulating senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)” by Sudipta Bar, Tyler A.U. Hilsabeck, Blaine Pattavina, José Alberto López-Domínguez, Nathan Basisty, Joanna Bons, Mark Watson, Birgit Schilling, Judith Campisi, Pankaj Kapahi and Amit Sharma, 20 March 2025, Aging.
DOI: 10.18632/aging.206224